 Global Information
Global InformationLung information
| Lung | |
|---|---|
 Diagram of the human lungs with the respiratory tract visible, and different colours for each lobe | |
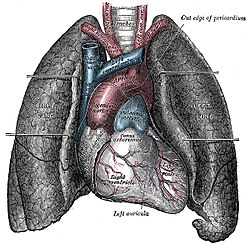 The human lungs flank the heart and great vessels in the chest cavity. | |
| Details | |
| System | Respiratory system |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | pulmo |
| Greek | πνεύμων (pneumon) |
| MeSH | D008168 |
| TA98 | A06.5.01.001 |
| TA2 | 3265 |
| Anatomical terminology [edit on Wikidata] | |
The lungs are the central organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the air and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. The pleurae, which are thin, smooth, and moist, serve to reduce friction between the lungs and chest wall during breathing, allowing for easy and effortless movements of the lungs.
Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their different muscles to support and foster breathing. In earlier tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the main muscle of respiration that drives breathing is the diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes vocal sounds including human speech possible.
Humans have two lungs, one on the left and one on the right. They are situated within the thoracic cavity of the chest. The right lung is bigger and heavier than the left, which shares space in the chest with the heart. The lungs together weigh approximately 1.3 kilograms (2.9 pounds). The lungs are part of the lower respiratory tract that begins at the trachea and branches into the bronchi and bronchioles, and which receive air breathed in via the conducting zone. The conducting zone ends at the terminal bronchioles. These divide into the respiratory bronchioles of the respiratory zone which divide into alveolar ducts that give rise to the alveolar sacs that contain the alveoli, where gas exchange takes place. Alveoli are also sparsely present on the walls of the respiratory bronchioles and alveolar ducts. Together, the lungs contain approximately 2,400 kilometres (1,500 miles) of airways and 300 to 500 million alveoli. Each lung is enclosed within a pleural sac of two membranes called pleurae; the membranes are separated by a film of pleural fluid, which allows the inner and outer membranes to slide over each other whilst breathing takes place, without much friction. The inner pleura also divides each lung into sections called lobes. The right lung has three lobes and the left has two. The lobes are further divided into bronchopulmonary segments and pulmonary lobules. The lungs have a unique blood supply, receiving deoxygenated blood from the heart in the pulmonary circulation for the purposes of receiving oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide, and a separate supply of oxygenated blood to the tissue of the lungs, in the bronchial circulation. Deoxygenated blood travels from the heart through the pulmonary artery to the lungs to be oxygenated in capillaries of alveoli. After the blood is oxygenated, it returns to the heart through the pulmonary vein to be sent to the rest of the body.[1][2]
The tissue of the lungs can be affected by a number of respiratory diseases, including pneumonia and lung cancer. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema, and can be related to smoking or exposure to harmful substances. A number of occupational lung diseases can be caused by substances such as coal dust, asbestos fibres, and crystalline silica dust. Diseases such as bronchitis can also affect the respiratory tract. Medical terms related to the lung often begin with pulmo-, from the Latin pulmonarius (of the lungs) as in pulmonology, or with pneumo- (from Greek πνεύμων "lung") as in pneumonia.
In embryonic development, the lungs begin to develop as an outpouching of the foregut, a tube which goes on to form the upper part of the digestive system. When the lungs are formed the fetus is held in the fluid-filled amniotic sac and so they do not function to breathe. Blood is also diverted from the lungs through the ductus arteriosus. At birth, however, air begins to pass through the lungs, and the diversionary duct closes, so that the lungs can begin to respire. The lungs only fully develop in early childhood.
- ^ Association, American Lung. "How Lungs Work". www.lung.org. Retrieved 2023-11-18.
- ^ Tucker, William D.; Weber, Carly; Burns, Bracken (2023), "Anatomy, Thorax, Heart Pulmonary Arteries", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 30521233, retrieved 2023-11-18