 Global Information
Global InformationLengyel culture information
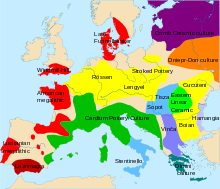 | |
| Horizon | Old Europe |
|---|---|
| Geographical range | Central Europe |
| Period | Neolithic, Chalcolithic |
| Dates | c. 5000 BC — c. 4000 BC |
| Major sites | Lengyel |
| Preceded by | Linear Pottery culture, Tisza culture |
| Followed by | Funnelbeaker culture, Baden culture, Globular Amphora culture |

The Lengyel culture is an archaeological culture of the European Neolithic, centered on the Middle Danube in Central Europe. It flourished from 5000 to 4000 BC, ending with phase IV, e.g., in Bohemia represented by the 'Jordanow/Jordansmühler culture'. It is followed by the Funnelbeaker culture/TrB culture[1] and the Baden culture. The eponymous type site is at Lengyel in Tolna county, Hungary.
It was preceded by the Linear Pottery culture and succeeded by the Corded Ware culture. In its northern extent, overlapped the somewhat later but otherwise approximately contemporaneous Funnelbeaker culture. Also closely related are the Stroke-ornamented ware and Rössen cultures, adjacent to the north and west, respectively.
Subgroups of the Lengyel horizon include the Austrian/Moravian Painted Ware I and II, Aichbühl, Jordanów/Jordanov/Jordansmühl, Schussenried, Gatersleben, etc.
It is a wide interaction sphere or cultural horizon rather than an archaeological culture in the narrow sense. Its distribution overlaps with the Tisza culture and with Stroke-Ornamented Pottery (STK) as far north as Osłonki, central Poland.
Lengyel pottery was found in western Hungary, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Austria, Poland, and Slovenia. Several Sopot culture finds in Croatia and Hungary were dated to the same general periods as the Lengyel culture finds. Influence in pottery styles is found even further afield, in parts of Germany and Switzerland.
Agriculture and stock raising (mainly cattle, but also pigs, and to a lesser extent, ovicaprids) was practiced, though many wild faunal remains have also been recovered. Settlements consisted of small houses as well as trapezoid longhouses. These settlements were sometimes open, sometimes surrounded by a defensive ditch.
Inhumation was in separate cemeteries, in the flexed position with apparently no preference for which side the deceased was laid out in.
Lengyel sites of the later period show signs of the use of copper in form of beads and hammered ribbons, marking the dawn of the Chalcolithic period in Central Europe.
It was associated with the cover-term Old Europe by Marija Gimbutas, though may have been undergone "kurganization" by the Proto-Indo-Europeans and become integrated into the successor Globular Amphora culture. According to archaeogenetic studies, its population had no or negligible amount of Indo-European steppe ancestry.
- ^ Mallory, James P.; Adams, Douglas Q., eds. (1997). Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture. Fitzroy Dearborn Publishers. pp. 349–50. ISBN 1884964982.