 Global Information
Global InformationGamma ray information
This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2024) |


| Nuclear physics |
|---|
 |
|
|
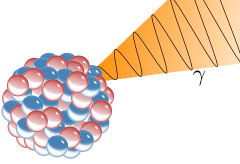
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol
γ
), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically shorter than those of X-rays. With frequencies above 30 exahertz (3×1019 Hz) and wavelength less than 10 picometer (1×10−11 m) gamma ray photons have the highest photon energy of any form of electromagnetic radiation. Paul Villard, a French chemist and physicist, discovered gamma radiation in 1900 while studying radiation emitted by radium. In 1903, Ernest Rutherford named this radiation gamma rays based on their relatively strong penetration of matter; in 1900, he had already named two less penetrating types of decay radiation (discovered by Henri Becquerel) alpha rays and beta rays in ascending order of penetrating power.
Gamma rays from radioactive decay are in the energy range from a few kiloelectronvolts (keV) to approximately 8 megaelectronvolts (MeV), corresponding to the typical energy levels in nuclei with reasonably long lifetimes. The energy spectrum of gamma rays can be used to identify the decaying radionuclides using gamma spectroscopy. Very-high-energy gamma rays in the 100–1000 teraelectronvolt (TeV) range have been observed from sources such as the Cygnus X-3 microquasar.
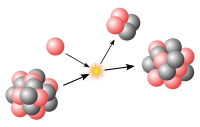
Natural sources of gamma rays originating on Earth are mostly a result of radioactive decay and secondary radiation from atmospheric interactions with cosmic ray particles. However, there are other rare natural sources, such as terrestrial gamma-ray flashes, which produce gamma rays from electron action upon the nucleus. Notable artificial sources of gamma rays include fission, such as that which occurs in nuclear reactors, and high energy physics experiments, such as neutral pion decay and nuclear fusion.
Gamma rays and X-rays are both electromagnetic radiation, and since they overlap in the electromagnetic spectrum, the terminology varies between scientific disciplines. In some fields of physics[specify], they are distinguished by their origin: Gamma rays are created by nuclear decay while X-rays originate outside the nucleus. In astrophysics, gamma rays are conventionally defined as having photon energies above 100 keV and are the subject of gamma ray astronomy, while radiation below 100 keV is classified as X-rays and is the subject of X-ray astronomy.
Gamma rays are ionizing radiation and are thus hazardous to life. They can cause DNA mutations, cancer and tumors, and at high doses burns and radiation sickness. Due to their high penetration power, they can damage bone marrow and internal organs. Unlike alpha and beta rays, they easily pass through the body and thus pose a formidable radiation protection challenge, requiring shielding made from dense materials such as lead or concrete. On Earth, the magnetosphere protects life from most types of lethal cosmic radiation other than gamma rays.