 Global Information
Global InformationDiscrete Fourier transform information
| Fourier transforms |
|---|
|

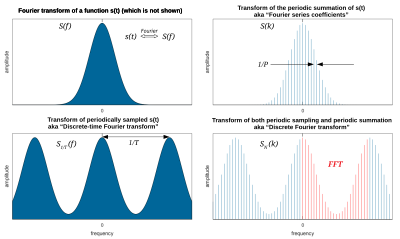
Left: A continuous function (top) and its Fourier transform (bottom).
Center-left: Periodic summation of the original function (top). Fourier transform (bottom) is zero except at discrete points. The inverse transform is a sum of sinusoids called Fourier series.
Center-right: Original function is discretized (multiplied by a Dirac comb) (top). Its Fourier transform (bottom) is a periodic summation (DTFT) of the original transform.
Right: The DFT (bottom) computes discrete samples of the continuous DTFT. The inverse DFT (top) is a periodic summation of the original samples. The FFT algorithm computes one cycle of the DFT and its inverse is one cycle of the DFT inverse.
In mathematics, the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) converts a finite sequence of equally-spaced samples of a function into a same-length sequence of equally-spaced samples of the discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT), which is a complex-valued function of frequency. The interval at which the DTFT is sampled is the reciprocal of the duration of the input sequence.[A][1] An inverse DFT (IDFT) is a Fourier series, using the DTFT samples as coefficients of complex sinusoids at the corresponding DTFT frequencies. It has the same sample-values as the original input sequence. The DFT is therefore said to be a frequency domain representation of the original input sequence. If the original sequence spans all the non-zero values of a function, its DTFT is continuous (and periodic), and the DFT provides discrete samples of one cycle. If the original sequence is one cycle of a periodic function, the DFT provides all the non-zero values of one DTFT cycle.
The DFT is the most important discrete transform, used to perform Fourier analysis in many practical applications.[2] In digital signal processing, the function is any quantity or signal that varies over time, such as the pressure of a sound wave, a radio signal, or daily temperature readings, sampled over a finite time interval (often defined by a window function[3]). In image processing, the samples can be the values of pixels along a row or column of a raster image. The DFT is also used to efficiently solve partial differential equations, and to perform other operations such as convolutions or multiplying large integers.
Since it deals with a finite amount of data, it can be implemented in computers by numerical algorithms or even dedicated hardware. These implementations usually employ efficient fast Fourier transform (FFT) algorithms;[4] so much so that the terms "FFT" and "DFT" are often used interchangeably. Prior to its current usage, the "FFT" initialism may have also been used for the ambiguous term "finite Fourier transform".
The DFT has many applications, including purely mathematical ones with no physical interpretation. But physically it can be related to signal processing as a discrete version (i.e. samples) of the discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT), which is a continuous and periodic function. The DFT computes N equally-spaced samples of one cycle of the DTFT. (see Fig.2 and § Sampling the DTFT)
Cite error: There are <ref group=upper-alpha> tags or {{efn-ua}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=upper-alpha}} template or {{notelist-ua}} template (see the help page).
- ^ Taboga, Marco (2021). "Discrete Fourier Transform - Frequencies", Lectures on matrix algebra. https://www.statlect.com/matrix-algebra/discrete-Fourier-transform-frequencies.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Strangwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Sahidullahwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Cooleywas invoked but never defined (see the help page).