 Global Information
Global Information1997 Asian financial crisis information
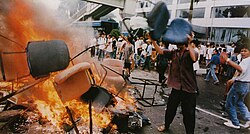
The 1997 Asian financial crisis was a period of financial crisis that gripped much of East and Southeast Asia during the late 1990s. The crisis began in Thailand in July 1997 before spreading to several other countries with a ripple effect, raising fears of a worldwide economic meltdown due to financial contagion.[1] However, the recovery in 1998–1999 was rapid, and worries of a meltdown quickly subsided.
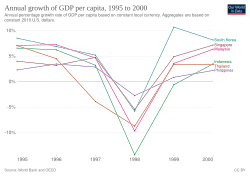
Originating in Thailand, where it was known as the Tom Yum Kung crisis (Thai: วิกฤตต้มยำกุ้ง) on 2 July, it followed the financial collapse of the Thai baht after the Thai government was forced to float the baht due to lack of foreign currency to support its currency peg to the U.S. dollar. Capital flight ensued almost immediately, beginning an international chain reaction. At the time, Thailand had acquired a burden of foreign debt.[2] As the crisis spread, other Southeast Asian countries and later Japan and South Korea saw slumping currencies, devalued stock markets and other asset prices, and a precipitous rise in private debt.[3][4] Foreign debt-to-GDP ratios rose from 100% to 167% in the four large Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) economies in 1993–96, then shot up beyond 180% during the worst of the crisis. In South Korea, the ratios rose from 13% to 21% and then as high as 40%, while the other northern newly industrialized countries fared much better. Only in Thailand and South Korea did debt service-to-exports ratios rise.[5]
South Korea, Indonesia and Thailand were the countries most affected by the crisis. Hong Kong, Laos, Malaysia and the Philippines were also hurt by the slump. Brunei, mainland China, Japan, Singapore, Taiwan, and Vietnam were less affected, although all suffered from a general loss of demand and confidence throughout the region. While Japan was slow to respond to requests from affected countries, China improved its reputation in the region through its contribution of $4 billion in bailout money, as well as its important decision not to de-value its own currency. Although most of the governments of Asia had seemingly sound fiscal policies, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) stepped in to initiate a $40 billion program to stabilize the currencies of South Korea, Thailand, and Indonesia, economies particularly hard hit by the crisis.[1]
The efforts to stem a global economic crisis did little to stabilize the domestic situation in Indonesia, however. After 30 years in power, Indonesian President Suharto was forced to step down on 21 May 1998 in the wake of widespread rioting that followed sharp price increases caused by a drastic devaluation of the rupiah. The effects of the crisis lingered through 1998, where many important stocks fell in Wall Street as a result of a dip in the values of the currencies of Russia and Latin American countries that weakened those countries' "demand for U.S. exports."[6] In 1998, growth in the Philippines dropped to virtually zero. Only Singapore proved relatively insulated from the shock, but nevertheless suffered serious hits in passing, mainly due to its status as a major financial hub and its geographical proximity to Malaysia and Indonesia. By 1999, however, analysts saw signs that the economies of Asia were beginning to recover.[7] After the crisis, economies in East and Southeast Asia worked together toward financial stability and better financial supervision.[8]
- ^ a b "Global Waves of Debt: Causes and Consequences". World Bank. Retrieved 13 May 2022.
- ^ "Asian Financial Crisis: When the World Started to Melt". EuroMoney. December 1997. Archived from the original on 8 June 2017. Retrieved 16 November 2015.
- ^ Yamazawa, Ippei (September 1998). "The Asian Economic Crisis and Japan" (PDF). The Developing Economies. 36 (3): 332–351. doi:10.1111/j.1746-1049.1998.tb00222.x. hdl:10.1111/j.1746-1049.1998.tb00222.x. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 16 November 2015.
- ^ Kaufman: pp. 195–6
- ^ "Key Indicators of Developing Asian and Pacific Countries 2003". Asian Development Bank. 34. August 2003. Archived from the original on 19 November 2015. Retrieved 16 November 2015.
- ^ TIME Annual 1998: The Year in Review. New York: TIME Books. 1999. p. 71. ISBN 1-883013-61-5. ISSN 1097-5721.
- ^ Pempel: pp 118–143
- ^ Kawai, Masahiro; Morgan, Peter J. (2012). "Central Banking for Financial Stability in Asia" (PDF). ADBI Working Paper 377. Tokyo: Asian Development Bank Institute. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 October 2012.