What is Neuropathy? It is a medical condition that damages or destroys the nerves in your body. Neuropathy often affects the peripheral nerves, those that are not attached directly to your brain. The peripheral nerves are the pathways that link to the brain through the spinal column.
The pathways (the motor nerves) enable the nerves (the information signals) to pass to and from your brain to your legs and hands. Neuropathy is often referred to as “nerve deafness” because the symptoms it causes often interfere with your ability to think, reason and move properly.
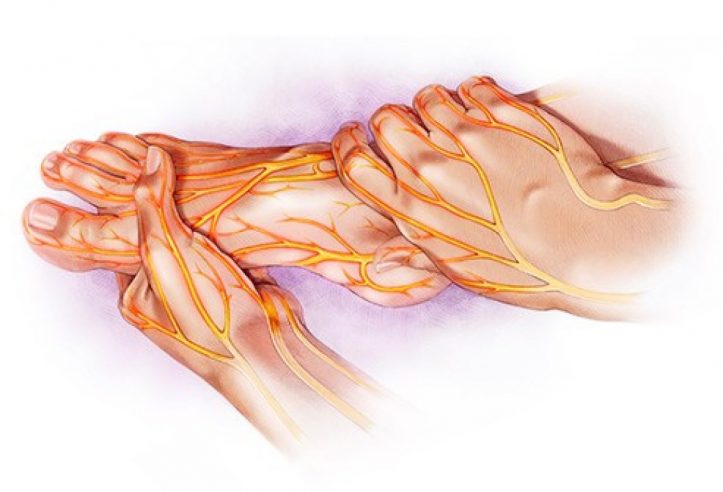
There are two main types of neuropathy – intrinsic and extrinsic. Intrinsic neuropathy is usually caused by disease, injury, infection or radiation therapy to the nerve. Intrinsic neuropathy often results in numbness, tingling or weakness of the muscles. Extrinsic neuropathy is caused by a lesion on one or more nerves. When these nerves are damaged, they do not receive the messages they normally receive and the messages get interrupted.
There are many causes of peripheral neuropathy. Many doctors refer to it as “indirect neuropathy.” Inherited diabetes is a major cause of peripheral neuropathy in many families. Diabetic neuropathy occurs when the body’s glucose or insulin levels are low enough to affect the functioning of its nerves.
Two disorders are known to cause neuropathy: rheumatoid arthritis and systemic sclerosis. Rheumatoid arthritis is an inflammatory disorder of the joints that can cause permanent damage. The disorder is associated with high levels of toxins that need to be removed from the body. Systemic sclerosis is a chronic autoimmune disease that destroys the body’s ability to produce an important protein, called a cytokine.
There are many treatment options for Neuropathy. These treatments include surgery, medications and health conditions. In most cases, surgery is used to remove damaged nerves. Medications can help control high blood sugar levels. Health conditions that include taking medications to lower blood sugar levels include diabetes insipidus and type I diabetes. In most cases, diabetes insipidus leads to diabetic neuropathy because the kidneys are unable to eliminate high amounts of fluids from the blood.
Symptoms of Neuropathy include leg pain, numbness and tingling sensations. A doctor will test the patient for nerve damage using an electroencephalograph (EEG). Changes in blood flow may also be evident using an MAST scan, magnetic resonance imaging or CT scan. Other symptoms include urinary or excretory problems, fatigue and decreased appetite. If the disorder is discovered at an early age, symptoms can be managed with simple diet and exercise modifications, physical therapy, or chiropractic treatments. However, if left untreated, severe neuropathy can result in permanent disability and death.
The term “neuropathy” refers to a disease that affects the nerves. This disease affects any part of the body, but is most common in the extremities such as the toes and fingers. In addition to these symptoms, patients can suffer from muscle weakness, muscle cramps, loss of balance and difficulty swallowing. It can lead to problems walking, getting dressed and rising from a seated position. The effects of diabetes on the body often affects peripheral nerves, but when these nerves are affected by neuropathy it is known as diabetic neuropathy.
There is no cure for neuropathy. However, there are medications that can help control and reduce the symptoms of neuropathy. When diabetes and alcoholism are co-occurring, the damage to nerves can be severe, resulting in diabetic neuropathy. It is important to keep the blood sugar levels in your body at an acceptable level, to avoid neuropathy. You should also ensure that you get plenty of exercise each day to maintain good health and prevent neuropathy from happening.