 Global Information
Global InformationParticle accelerator information
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (November 2022) |

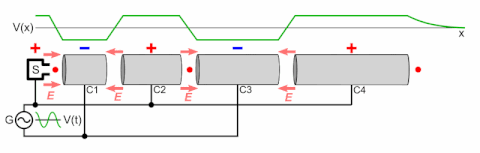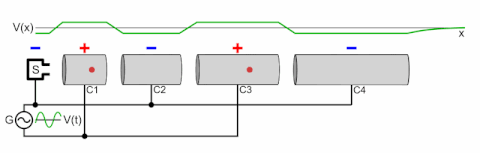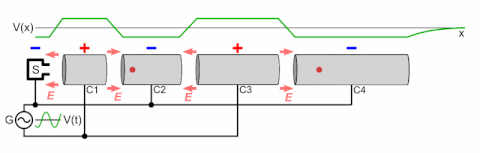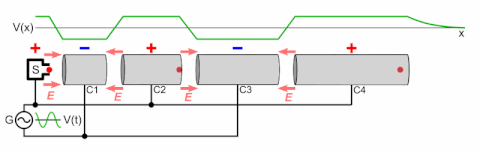
A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel charged particles to very high speeds and energies, and to contain them in well-defined beams.[1][2]
Large accelerators are used for fundamental research in particle physics. The largest accelerator currently active is the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) near Geneva, Switzerland, operated by CERN. It is a collider accelerator, which can accelerate two beams of protons to an energy of 6.5 TeV and cause them to collide head-on, creating center-of-mass energies of 13 TeV. Other powerful accelerators are RHIC at Brookhaven National Laboratory in New York and, formerly, the Tevatron at Fermilab, Batavia, Illinois. Accelerators are also used as synchrotron light sources for the study of condensed matter physics. Smaller particle accelerators are used in a wide variety of applications, including particle therapy for oncological purposes, radioisotope production for medical diagnostics, ion implanters for the manufacture of semiconductors, and accelerator mass spectrometers for measurements of rare isotopes such as radiocarbon. There are currently more than 30,000 accelerators in operation around the world.[3][4]
There are two basic classes of accelerators: electrostatic and electrodynamic (or electromagnetic) accelerators.[5] Electrostatic particle accelerators use static electric fields to accelerate particles. The most common types are the Cockcroft–Walton generator and the Van de Graaff generator. A small-scale example of this class is the cathode ray tube in an ordinary old television set. The achievable kinetic energy for particles in these devices is determined by the accelerating voltage, which is limited by electrical breakdown. Electrodynamic or electromagnetic accelerators, on the other hand, use changing electromagnetic fields (either magnetic induction or oscillating radio frequency fields) to accelerate particles. Since in these types the particles can pass through the same accelerating field multiple times, the output energy is not limited by the strength of the accelerating field. This class, which was first developed in the 1920s, is the basis for most modern large-scale accelerators.
Rolf Widerøe, Gustav Ising, Leó Szilárd, Max Steenbeck, and Ernest Lawrence are considered pioneers of this field, having conceived and built the first operational linear particle accelerator,[6] the betatron, and the cyclotron.
Because the target of the particle beams of early accelerators was usually the atoms of a piece of matter, with the goal being to create collisions with their nuclei in order to investigate nuclear structure, accelerators were commonly referred to as atom smashers in the 20th century.[7] The term persists despite the fact that many modern accelerators create collisions between two subatomic particles, rather than a particle and an atomic nucleus.[8][9][10]
- ^ Chao, Alexander W; Chou, Weiren (2008). Reviews of Accelerator Science and Technology: Volume 1. Singapore: World Scientific. Bibcode:2008rast.book.....C. doi:10.1142/7037. ISBN 978-981-283-520-8.
- ^ Livingston, M. S.; Blewett, J. (1969). Particle Accelerators. New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-1-114-44384-6.
- ^ "More background on accelerators". www.iaea.org. 2016-10-12. Retrieved 2023-11-10.
- ^ Witman, Sarah (15 April 2014). "Ten things you might not know about particle accelerators". Symmetry Magazine. Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory. Retrieved 21 April 2014.
- ^ Humphries, Stanley (1986). Principles of Charged Particle Acceleration. Wiley-Interscience. p. 4. ISBN 978-0471878780.
- ^ Sessler, Andrew; Wilson, Edmund (2014). Engines of Discovery: A Century of Particle Accelerators Revised and Expanded Edition. World Scientific. Bibcode:2014edcp.book.....S. doi:10.1142/8552. ISBN 978-981-4417-18-1.
- ^ "six Million Volt Atom Smasher Creates New Elements". Popular Mechanics: 580. April 1935.
- ^ Higgins, A. G. (December 18, 2009). "Atom Smasher Preparing 2010 New Science Restart". U.S. News & World Report.
- ^ Cho, A. (June 2, 2006). "Aging Atom Smasher Runs All Out in Race for Most Coveted Particle". Science. 312 (5778): 1302–1303. doi:10.1126/science.312.5778.1302. PMID 16741091. S2CID 7016336.
- ^ "Atom smasher". American Heritage Science Dictionary. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. 2005. p. 49. ISBN 978-0-618-45504-1.