 Global Information
Global InformationNordic Bronze Age information
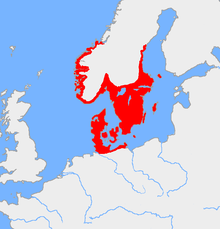 | |
| Geographical range | Southern Scandinavia, northern Germany |
|---|---|
| Period | Bronze Age |
| Dates | c. 2000/1750–500 BC |
| Preceded by | Battle Axe culture, Bell Beaker culture, Pitted Ware culture, Nordic Stone Age |
| Followed by | Jastorf culture, Pre-Roman Iron Age, Iron Age Scandinavia |
| Part of a series on |
| Scandinavia |
|---|
 |
|
The Nordic Bronze Age (also Northern Bronze Age, or Scandinavian Bronze Age) is a period of Scandinavian prehistory from c. 2000/1750–500 BC.
The Nordic Bronze Age culture emerged about 1750 BC as a continuation of the Battle Axe culture (the Scandinavian Corded Ware variant) and Bell Beaker culture,[1][2] as well as from influence that came from Central Europe.[3] This influence most likely came from people similar to those of the Unetice culture, since they brought customs that were derived from Unetice or from local interpretations of the Unetice culture located in North Western Germany.[4] The metallurgical influences from Central Europe are especially noticeable.[5][6] The Bronze Age in Scandinavia can be said to begin shortly after 2000 BC with the introduction and use of bronze tools, followed by a more systematic adoption of bronze metalworking technology from 1750 BC.[7][8][9]
The Nordic Bronze Age maintained close trade links with Mycenaean Greece, with whom it shares several striking similarities.[10][11][3][12] Some cultural similarities between the Nordic Bronze Age, the Sintashta/Andronovo culture and peoples of the Rigveda have also been detected.[a][13] The Nordic Bronze Age region included part of northern Germany,[14] and some scholars also include sites in what is now Estonia, Finland and Pomerania as part of its cultural sphere.[15][16]
The people of the Nordic Bronze Age were actively engaged in the export of amber, and imported metals in return, becoming expert metalworkers. With respect to the number and density of metal deposits, the Nordic Bronze Age became the richest culture in Europe during its existence.[17][18][19]
Iron metallurgy began to be practised in Scandinavia during the later Bronze Age, from at least the 9th century BC.[20] Around the 5th century BC, the Nordic Bronze Age was succeeded by the Pre-Roman Iron Age and the Jastorf culture. The Nordic Bronze Age is often considered ancestral to the Germanic peoples.[21]
- ^ Kristiansen, Kristian (2009). "Proto-Indo-European Languages and Institutions: An Archaeological Approach". In van der Linden, M.; Jones-Bley, C. (eds.). Journal of Indo-European Studies Monograph Series, No. 56: Departure from the Homeland. pp. 111–140. Archived from the original on 29 September 2022. Retrieved 2 May 2023.
- ^ Kristiansen, Kristian; Larsson, Thomas B. (2005). The Rise of Bronze Age Society. Cambridge University Press. p. 141. ISBN 9780521843638. Archived from the original on 29 March 2023. Retrieved 21 December 2021.
The Early Bronze Age societies that evolved after 2000 BC thus inherited their basic social and cosmological order from the Beaker and Battle-Axe cultures of the third millennium BC.
- ^ a b Vandkilde, Helle (April 2014). "Breakthrough of the Nordic Bronze Age: Transcultural Warriorhood and a Carpathian Crossroad in the Sixteenth Century BC". European Journal of Archaeology. 17 (4): 602–633. doi:10.1179/1461957114Y.0000000064. S2CID 162256646. Archived from the original on 22 July 2022. Retrieved 30 November 2020.
- ^ Johannsen, Jens (2017). "Mansion on the Hill – A Monumental Late Neolithic House at Vinge, Zealand, Denmark". Journal of Neolithic Archaeology. 19. Archived from the original on 20 April 2023. Retrieved 2 May 2023.
- ^ Bergerbrant, Sophie (May 2007). "Bronze Age Identities: Costume, Conflict and Contact in Northern Europe 1600–1300 BC" (PDF). Stockholm Studies in Archaeology (43): 7–201. Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 July 2022. Retrieved 30 November 2020 – via diva-portal.org.
- ^ Ling, Johan; Persson, Per-Olof; Billström, Kjell (14 March 2013). "Moving metals II: provenancing Scandinavian Bronze Age artefacts by lead isotope and elemental analyses" (PDF). Journal of Archaeological Science. 41: 107–129. Bibcode:2014JArSc..41..106L. doi:10.1016/j.jas.2013.07.018. Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 March 2022. Retrieved 30 November 2020 – via shfa.se.
- ^ Kristiansen, Kristian (2010). "Decentralized Complexity: The Case of Bronze Age Northern Europe". Pathways to Power. Fundamental Issues in Archaeology. Springer, New York, NY. pp. 169–192. doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-6300-0_7. ISBN 978-1-4419-6299-7. Archived from the original on 5 April 2023. Retrieved 26 September 2022.
The northern Bronze Age may be said to begin shortly after 2000 BC with the introduction and use of simple bronze tools, especially axes. At the same time, huge longhouses for large (chiefly) households emerged. With the more systematic adoption of metalworking bronze technology after 1750 BC, a diversified use of new tools, weapons, and ornaments made of bronze appeared, together with a new warrior elite.
- ^ Vandkilde, Helle (2004). "Bronze Age Scandinavia". In Bogucki, Peter; Crabtree, Pam J. (eds.). Ancient Europe, 8000 B.C. to A.D. 1000: Encyclopedia of the Barbarian World. Charles Scribner's Sons. p. 73. ISBN 0-684-80668-1.
The Bronze Age proper commenced c. 1700 B.C. and concluded c. 500 B.C., but metals became socially integrated by about 2000 B.C., during the Late Neolithic period—already a bronze age in all but name.
- ^ Nørgaard, HW; Pernicka, E; Vandkilde, H (2019). "On the trail of Scandinavia's early metallurgy: Provenance, transfer and mixing". PLOS ONE. 14 (7): e0219574. Bibcode:2019PLoSO..1419574N. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0219574. PMC 6655661. PMID 31339904.
As early as c. 4400 BC, there are signs of a faint awareness of copper technologies in Scandinavia in the form of rare imports of copper axes into the region's Late Mesolithic communities. A thousand years later, local metallurgy was likely practiced in the Middle Neolithic Funnelbeaker culture, only to disappear again subsequently. During most of the third millennium, metallurgy seems absent from the region, even if experiments with casting copper axes and hammering sheet ornaments reappear in Bell Beaker environments in Jutland, 2400–2100 BC. ... At 2000 BC, however, a copper-based technology begins to achieve full economic and social integration in Scandinavia simultaneously with the spread of bronze, or copper with similar properties, across Europe
- ^ Kristiansen & Suchowska-Ducke 2015, pp. 371–372.
- ^ Gubanov 2012, pp. 99–103.
- ^ Kristiansen, Kristian; Larsson, Thomas B. (2005). The Rise of Bronze Age Society. Cambridge University Press. p. 342. ISBN 9780521843638. Archived from the original on 29 March 2023. Retrieved 21 December 2021.
In the Nordic Bronze Age of period 2 one finds more east Mediterranean and Mycenaean influences in metalwork, prestige goods and cosmology than in any other region in Europe.
- ^ Kristiansen, Kristian (2011). "Bridging India and Scandinavia: Institutional Transmission and Elite Conquest during the Bronze Age". Interweaving worlds systemic interactions in Eurasia, 7th to 1st millennia BC. Oxbow Books. pp. 243–265. ISBN 978-1-84217-998-7. Archived from the original on 27 December 2021. Retrieved 27 December 2021.
- ^ Vandkilde, Helle (2004). "Bronze Age Scandinavia". In Bogucki, Peter; Crabtree, Pam J. (eds.). Ancient Europe, 8000 B.C. to A.D. 1000: Encyclopedia of the Barbarian World. Charles Scribner's Sons. p. 73. ISBN 0-684-80668-1.
The core region of the classic Nordic Bronze Age is southern Scandinavia, consisting of Denmark, Schleswig, and Scania. The adjoining northern European lowland in present-day Germany, as well as southern Norway and south-central Sweden, can be considered to be closely associated.
- ^ Minkevičius, Karolis; Podėnas, Vytenis; Urbonaitė-Ubė, Miglė; Ubis, Edvinas; Kisielienė, Dalia (1 May 2020). "New evidence on the southeast Baltic Late Bronze Age agrarian intensification and the earliest AMS dates of Lens culinaris and Vicia faba". Vegetation History and Archaeobotany. 29 (3): 327–338. doi:10.1007/s00334-019-00745-2. ISSN 1617-6278. S2CID 202194880. Archived from the original on 10 February 2023. Retrieved 30 November 2020.
- ^ "Bronze Age - Finland - SpottingHistory.com". www.spottinghistory.com. Archived from the original on 20 October 2020. Retrieved 30 November 2020.
- ^ Kristiansen & Suchowska-Ducke 2015, p. 369.
- ^ Frei 2019.
- ^ Kristiansen, Kristian; Larsson, Thomas B. (2005). The Rise of Bronze Age Society. Cambridge University Press. p. 249. ISBN 9780521843638. Archived from the original on 29 March 2023. Retrieved 21 December 2021.
Qualitatively the artistic and technical expressions [of the Nordic Bronze Age] are above anything in Europe except Minoan/Mycenaean culture; quantitatively there is no region in Europe with such an accumulation of high-quality weapons and ornaments during the period 1500–1000 BC, and that includes the Minoan/Mycenaean culture.
- ^ Lund, Julie; Melheim, Lene (2011). "Heads and Tails – Minds and Bodies: Reconsidering the Late Bronze Age Vestby Hoard". European Journal of Archaeology. 14 (3): 441–464. doi:10.1179/146195711798356692. S2CID 162289964. Archived from the original on 14 September 2023. Retrieved 11 August 2023.
iron technology was practiced in the Nordic region from at least the ninth century BC (Hjärthner-Holdar 1993; Serning 1984)
- ^ Schmidt 1991, pp. 129–133.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).